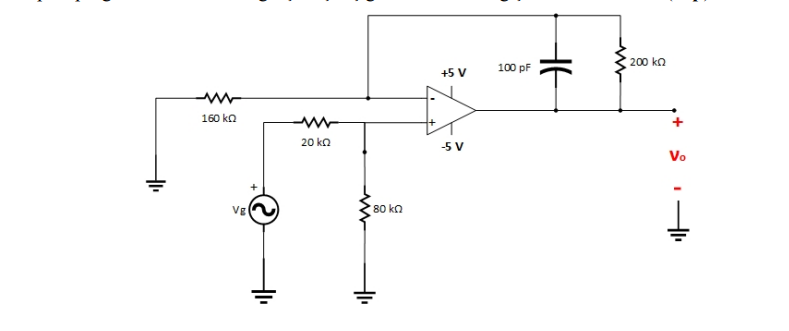
Solved Design an operational amplifier circuit that performs Circuit Diagram Op-amp Basics (part 1): Operational amplifiers (op-amps) are some of the most important, widely used, and versatile circuits in use today. especially with even higher gains. Image 8 shows a circuit design that will allow for a very high input impedance (1MΩ) and high gain (-102), but that can still be built with readily available parts the op amp's place in the world of analog electronics. Chapter 2 reviews some basic phys-ics and develops the fundamental circuit equations that are used throughout the book. Similar equations have been developed in other books, but the presentation here empha-sizes material required for speedy op amp design. The ideal op amp equations are devel-

The circuitry that makes up an op-amp consists of transistors, resistors, diodes, and a couple capacitors. In general, these components are combined to achieve within the op-amp two stages of differential amplifiers and a common-collector amplifier. [1] In an effort to simplify the operational amplifier, one must not forget that the Basic OpAmp Design Release 2.0 Oct 20, 2018. Many newcomers into electronics, especially those in the digital world, are often intimidated by opamps (operational amplifiers). They are quite simple but most explanations on how they work confuse the hobbyist. A basic circuit uses two resistors. An input resistor (Rin) and a feedback resistor

Ultimate Guide to Op Circuit Diagram
In this chapter we will discuss the basic operation of the op amp, one of the most common linear design building blocks. In section 1 the basic operation of the op amp will be discussed. We will concentrate on the op amp from the black box point of view. There are a good many texts that describe the internal workings of an op amp, so in this Offset voltage: The DC voltage that, when applied between the input pins, will cause a DC output voltage of zero. If both inputs were grounded, the output voltage of the op-amp would not be zero. Slew rate: The time taken for the output to change for a given input.Specified as V/mS. Equivalent input noise voltage: The noise performance of the op-amp. An ideal voltage source is placed in series Operational Amplifier Circuits Review: Ideal Op-amp in an open loop configuration Ro Ri + _ Vp Vn Vi + _ AVi + Vo Ip In An ideal op-amp is characterized with infinite open-loop gain A→∞ The other relevant conditions for an ideal op-amp are: 1. Ip =In =0 2. Ri =∞ 3. Ro =0 Ideal op-amp in a negative feedback configuration When an op-amp
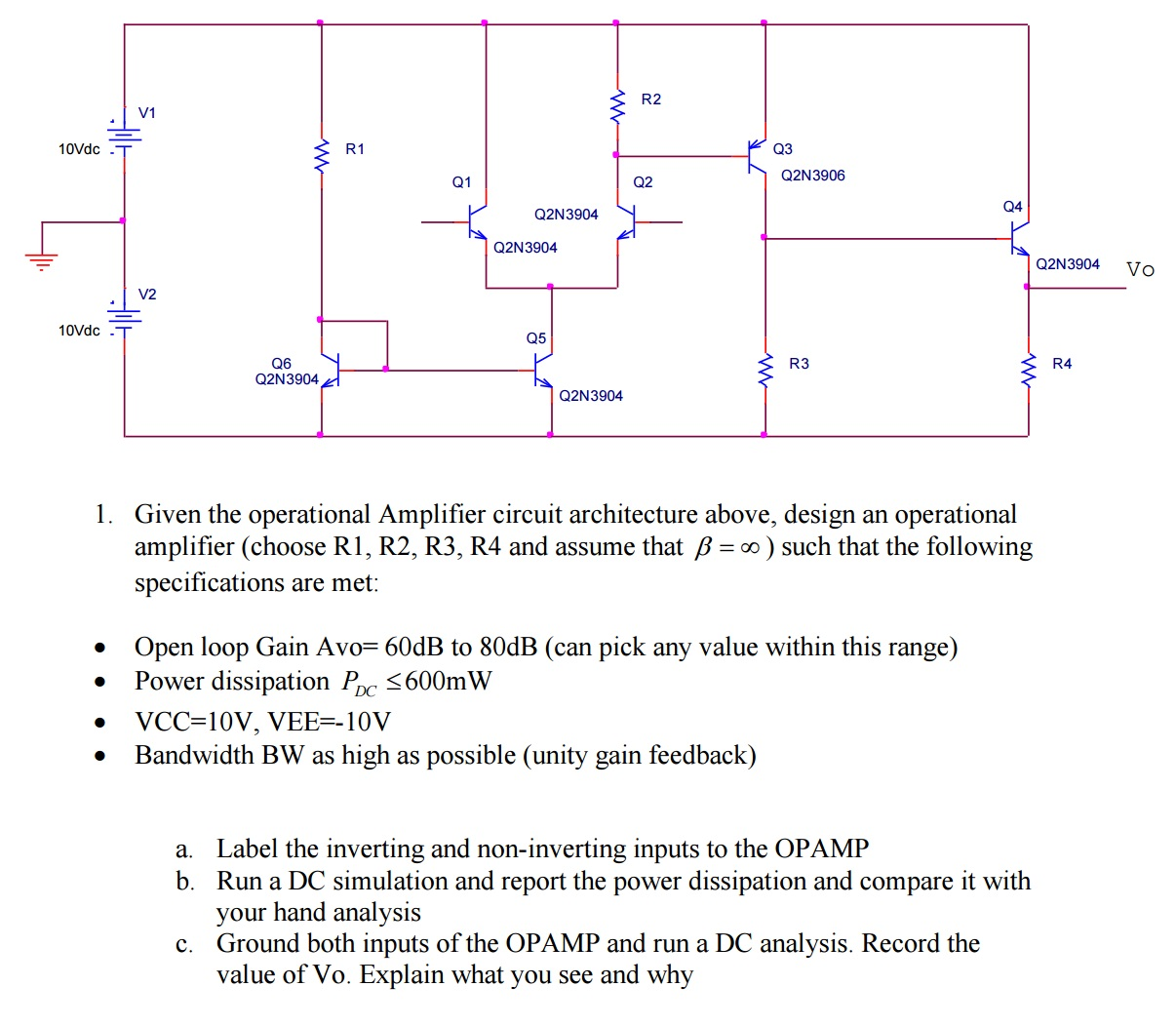
The circuit operates from a dual supply +Vcc and -Vee which ensures a constant supply. The voltage that appears at the output, Vout of the amplifier is the difference between the two input signals as the two base inputs are in anti-phase with each other. So as the forward bias of transistor, TR1 is increased, the forward bias of transistor TR2 is reduced and vice versa.
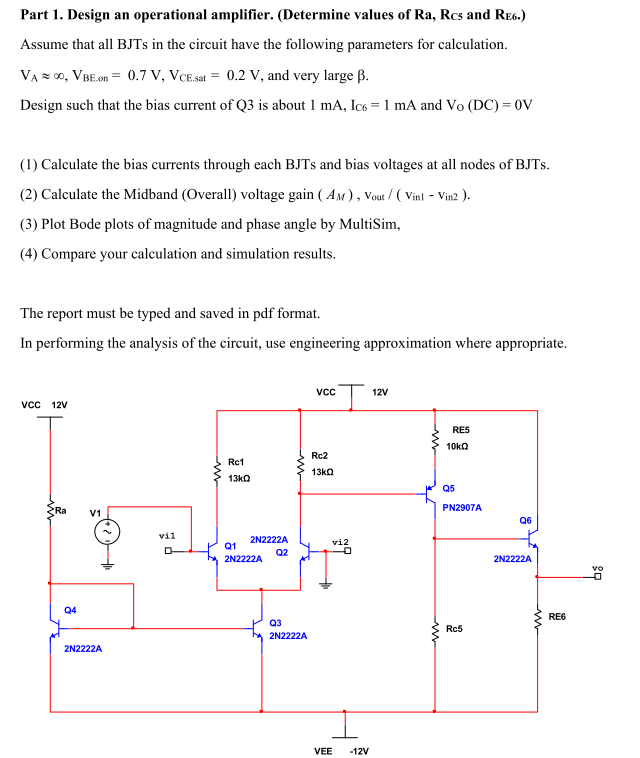
Top 10 Fundamental Operational Amplifier Circuits Circuit Diagram
An op-amp has two inputs, an inverting terminal (labeled „-") and a non-inverting terminal (labeled „+"). And has a single output. The first input is called inverting because the output voltage is inverse of the voltage applied at the inverting input, times the gain of the amplifier circuit.If we apply the signal to the non-inverting input we get the same signal on the output, times gain.