Noise Reduction Circuit Diagram It can be "shot noise" which is produced in active devices from the electron flow through the device, atmospheric noise, EMI from switching power supplies, radio transmitters and other electronic devices. There are many ways to cut down on noise in circuits which involve using decoupling capacitors, filters and shielding. Conductive coupling occurs due to the noise conduction along the wires between the source and the circuit elements. Capacitive coupling occurs in the following way. Let's assume that we have a noise source with a noise conducting wire. If the noise conducting wire is too close to the circuit conductor, it can create the electric fied, forming Make use of multistage filter to attenuate multiband power supply noise. Also refer Power supply noise reduction techniques>>. Conclusion. Implementing effective noise reduction techniques can improve signal integrity and overall system performance. Understanding these methods ensures robust and reliable electronic designs.
Electrical noise occurs when electrical signals produce undesirable effects in the electronic circuits of the control system. This guide discuss how to identify and correct electrical noise issues. and those carrying dc (low voltage level) signals will effectively reduce the noise in sensitive circuits. 4. Electromagnetic (radiation) coupling . The adverse effects of noise on electronic circuits, including power supplies, are well documented and thus, worthy of this lofty concern. So, why does noise warrant agonizing over a design? The initial cause for concern is the unpredictability of the noise itself. In general, noise can arise from either an external source or an internal source. Analog circuits are key in today's electronics, from audio to medical devices. They face noise and electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can harm their performance. This article will cover how to reduce these effects using transistors. Negative feedback is a strong tool for noise reduction in analog circuits. It compares the output to
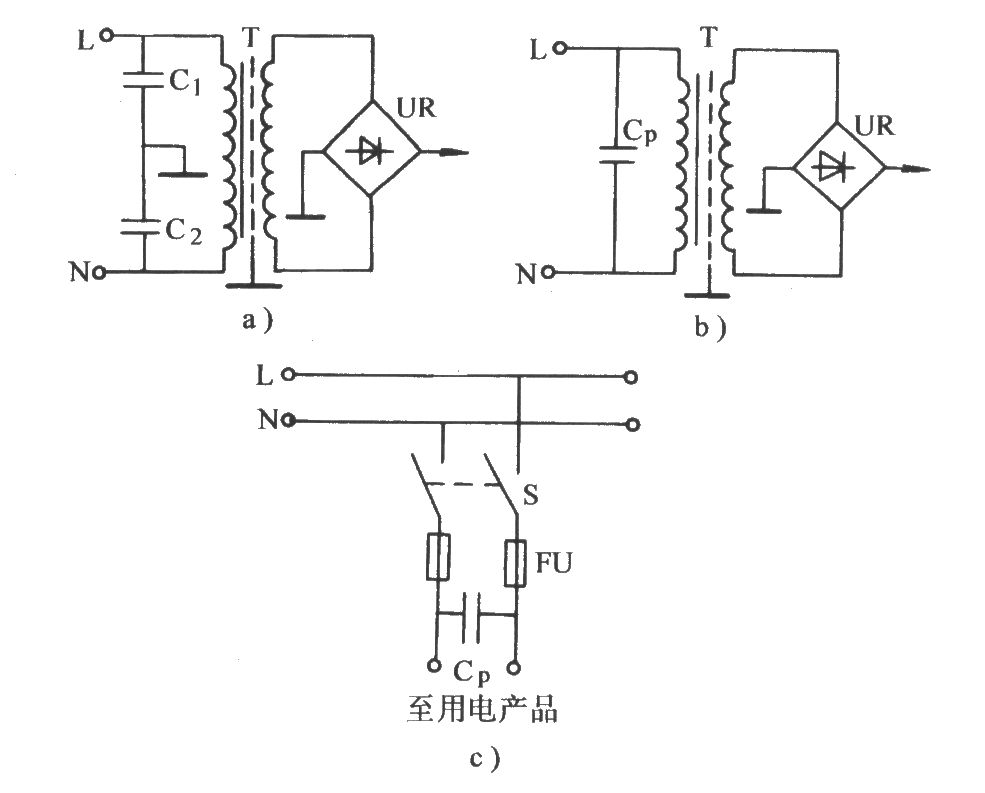
How to reduce noise in an electrical circuit Circuit Diagram
%PDF-1.3 %Äåòåë§ó ÐÄÆ 4 0 obj /Length 5 0 R /Filter /FlateDecode >> stream x WMO G ½÷¯¨Ü K ý1Ó3"£q¤8R¤ Vâ å`- l 1»¶¬ä×çUOWõ|° †ÒÎV×TU×{õºy 3z K¶²øñÁ×Mç¨mûªëmOMmi{E ô™NNwŽ6;réw·ÁKMè« ?t—ÞàG£¶[µåàÁ¶}è Ýjºb¹¡ë7"JB ¡ŽÑ 'S-C‰y QÆErõ.EFÅòåFJt}¤;"ë ¡ç‚BÓ÷¡îÊ `ëlèCÄ®e_ $ Uïú¦Ø81l Söš White noise has an equal power per Hertz so looks like a flat, horizontal line of a spectrum analyzer. White light would also have a uniform power density. "Pink" noise refers to noise where the noise power density per Hertz is inversely proportional to the frequency. So, the noise increases with lower frequency. 5. Case Study: Noise Reduction in a Sensor Circuit. To illustrate the principles discussed, let's consider a case study of noise reduction in a sensor circuit: 5.1 Problem Statement. A temperature sensor circuit is experiencing noise, leading to inaccurate readings. The noise is primarily due to power supply fluctuations and crosstalk from